- home
- wto membership
- accessions
- training module
- negotiation of market access concessions and commitments
Click the + to open an item.
5.3 Negotiation of market access concessions and commitments
Services Schedule back to top
This section first examines the format for Services Schedules and then provides an overview of the specific commitments undertaken by applicants that have acceded to the WTO.
Notes on the drafting of Services Schedules and the format used for such Schedules are contained in Annex 9.
Overview of specific commitments undertaken by new Members
The complexity of the services commitments means that any attempt to summarize them involves radical simplification.
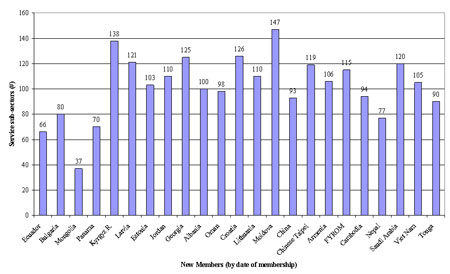
Table 10 below is based on a total of approximately 160 service sub-sectors and shows that there is quite a wide variation in the number of sub-sectors on which acceding Members have made commitments. Among the points that stand out are:
- The Schedules of specific commitments of the first four governments to accede cover a lower number of sectors than subsequent accessions.
- The two LDCs made commitments in 94 and 77 sub-sectors, respectively or approximately 58 percent and 48 percent of all sub-sectors. Tonga made commitments in 90 sub-sectors.
- Apart from the first four governments to accede, LDCs, and Tonga, there is a wide spread in the commitments made by the remaining 16 new Members: from 93 sub-sectors in the case of China (about the same number as one of the LDCs) to 147 sub-sectors for Moldova.
- The number of sub-sectors in which commitments were made by these 16 new Members does not appear to correlate with any of the more obvious criteria that might be used to discern a pattern in these results (date of accession, GDP, GDP per capita).
Note: The number of GATS services sectors with commitments has been estimated by the WTO Secretariat on the basis of available information and in the light of the Services Sectoral Classification List (WTO document MTN.GNS/W/120).
Source: WTO.
The above analysis does not tell us which sectors were committed. Table 11 below identifies whether the new Members made specific commitments in 26 basic groups of services sectors. This shows that the Schedules of acceders have not only a high sectoral coverage but that they usually made commitments in key sectors.
- The first four countries to accede made specific commitments in 11 to 21 of these sectors. These accessions are little guide to current practice.
- The two LDCs that have acceded made commitments in 19 and 22 sectors, respectively.
- The other 17 governments made commitments in 22 to 26 sectors ?on average, 24 of the 26 sectors.
Leaving aside the first four countries to accede, it will be seen that all of the other 19 acceders (including LDCs) made at least some commitments in the following sectors: professional services (legal, accountancy, architectural and engineering); computer and related services; courier services; telecommunications (value-added and basic)?financial services (insurance, banking and other); tourism; and air transport465. Fewer made commitments in postal services (6); audiovisual services (11); rail transport(13); maritime transport (15); and road transport (16).
| Acceded Member Service Sector | Ecuador | Bulgaria | Mongolia | Panama | Kyrgyz Republic | Latvia | Estonia | Jordan | Georgia | Albania | Oman | Croatia | Lithuania | Moldova | China | Chinese Taipei | Armenia | The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia | Nepal (LDC) | Cambodia (LDC) | Saudi Arabia | Viet Nam | Tonga |
| Professional: ?legal |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| ?accountancy |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| ?taxation |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ?architectural and engineering |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| ?medical |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Computer and related |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| R&D |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other business |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Communication: Postal |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Courier |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Telecom: ?valued added |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| ?basic |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Audiovisual466 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Distribution |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Educational |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Environmental |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial: ?insurance |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| ?banking and other |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Health and Social |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Tourism |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Recreational |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport: ?Maritime transport |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| ?Air transport |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| ?Rail transport |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ?Road transport |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| TOTAL SECTORS 26 | 18 | 21 | 11 | 18 | 26 | 23 | 24 | 23 | 25 | 23 | 22 | 24 | 24 | 25 | 21 | 23 | 24 | 22 | 19 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 22 |
MFN Exemptions: all except Mongolia, Kyrgyz Republic and Oman.
A different sort of analysis is necessary to obtain an idea of the quality of the commitments made. It is beyond the scope of this Handbook to enter into a detailed analysis of all the specific commitments undertaken by new Members in their Schedules, but a few points stand out. First, commitments by new Members tend, overall, to have fewer limitations attached to them than those of older Members. Second, sectors committed are more often 憉nbound?under mode 1 (cross-border trade) than under other modes, while commitments under mode 2 (consumption abroad) tend to be unrestricted. Third, a relatively higher number of limitations tend to be attached to commitments under modes 3 (commercial presence) and 4 (movement of natural persons). Examples of limitations under mode 3 include foreign equity limits, restrictions on the type of legal entity and limitations on the number of suppliers. Mode 4 commitments are usually set out in the horizontal section of the Schedule. Commitments cover some or all of the following categories of natural persons: intra-corporate transferees in senior management, executive or specialist positions; services salespersons; persons responsible for setting up a commercial presence; contractual service suppliers (employees of juridical persons) and independent professionals. These categories are usually defined in the horizontal section, which also specifies the length of stay permitted and any other market access or national treatment limitations.
While the importance of the different modes varies from sector to sector it has been estimated that mode 1 accounts for about 35 percent of commercial services trade, mode 2 for 10 to 15 percent, mode 3 for about 50 percent and mode 4 for 1-2 percent of such trade.467
Notes:
465.
Recall that the GATS coverage of this sector is limited. back to text
466. Audiovisual services commitments have often been reflected in both the specific commitments in this sector and the list of MFN exemptions. back to text
467. WTO International Trade Statistics, 2005, p.8. back to text