- home
- trade topics
- agriculture
Agriculture
Trade and markets for food and farm goods matter to us all — whether we are consumers of these products, or also produce, transform and trade them.
To address government policies that distort markets and restrict trade, WTO members concluded the Agreement on Agriculture, which came into force in 1995. This initiated reductions in subsidies and trade barriers to make markets fairer and more competitive. It also provided for members to continue negotiations for further reform, taking into account concerns such as food security and the environment. These ongoing talks led in 2015 to a historic decision to abolish agricultural export subsidies and new rules for other forms of farm export support.
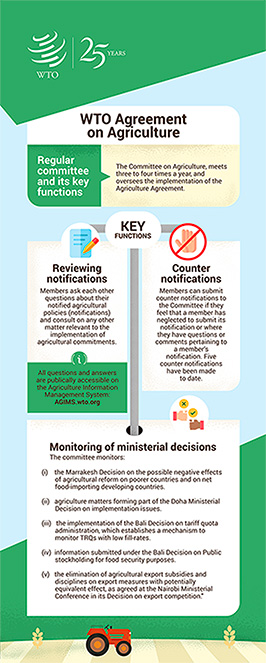
The WTO's Agriculture Committee oversees implementation of the Agreement and provides a forum for members to address related concerns.
See also:
Sanitary and phytosanitary measures
i.e. food safety and animal-plant health
Standards and Trade Development Facility
Helping developing countries meet food and health standards
Fact sheets
- ?a href="/english/tratop_e/agric_e/agboxes_e.htm">The boxes?in domestic support
- Export subsidies and other export support measures
- An unofficial guide to agricultural safeguards
Glossary
News
See news on the agriculture negotiations
See news on cotton
Introduction
The WTO Agriculture Agreement provides a framework for the long-term reform of agricultural trade and domestic policies, with the aim of leading to fairer competition and a less distorted sector.
The Agreement covers:
- Market access — the use of trade restrictions, such as tariffs on imports
- Domestic support — the use of subsidies and other support programmes that directly stimulate production and distort trade
- Export competition — the use of export subsidies and other government support programmes that subsidize exports.
Under the Agreement, WTO members agree to “schedules” or lists of commitments that set limits on the tariffs they can apply to individual products and on levels of domestic support and export subsidies.
back to topCommittee on Agriculture
The Committee on Agriculture oversees the implementation of the Agreement on agriculture and provides a forum for members to raise and address related questions and concerns. The current chair is .
Full details back to topAgriculture negotiations
Agricultural trade reform did not end with the birth of the Agriculture Agreement. WTO members are continuing to negotiate agricultural trade reform.
WTO members adopted important decisions on agriculture at the 2015 WTO Ministerial Conference in Nairobi, Kenya. These include a commitment to abolish subsidies for farm exports as well as decisions on public stockholding for food security purposes, on a special safeguard mechanism for developing countries, and on trade rules for cotton.
At the 2013 WTO Ministerial Conference in Bali, Indonesia, ministers also agreed on a package of issues in agriculture.
Cotton
Cotton is discussed at the WTO on two tracks: 1) the trade reforms needed to address subsidies and high trade barriers for cotton, and 2) the assistance provided to the cotton sector in developing countries.
Food security
The WTO Agreement on Agriculture explicitly recognises the need to take account of food security — both in the commitments that WTO members have made, and in ongoing negotiations.
back to topCOVID-19 and agriculture
- COVID-19: Agricultural measures
- WTO members' proposals on COVID-19
- Submissions by intergovernmental organizations
Find out more
Introduction to agricultural trade in the WTO
Links to the agriculture section of the WTO guide “Understanding the WTO”
Summary of the Agriculture Agreement
A technical summary
Explanation of the Agriculture Agreement
A more detailed 8-part technical introduction
Announcing Hackathon on International Trade and Food Security - Registration closes 1 July 2025. All details can be found here:
Guidelines
The WTO's regular food and farm policy trade news round-up
Videos
Problems viewing this page? If so, please contact [email protected] giving details of the operating system and web browser you are using.